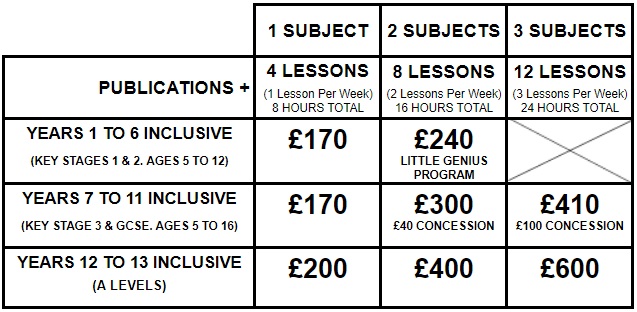
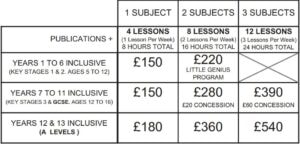
Core
1 Identify and name on diagrams of the male reproductive system: the testes, scrotum, sperm ducts, prostate gland, urethra and penis
2 State the function of the parts of the male reproductive system limited to: – testes – production of male gametes (sperm)
– scrotum
– sac that holds the testes outside the body
– sperm ducts
– transfer sperm to the urethra
– prostate gland
– secrete fluids for sperm to swim in forming semen
– urethra
– carries urine and semen out of the body
– penis
– transfers semen to vagina during sexual intercourse
3 Identify and name on diagrams of the female reproductive system: the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix and vagina
4 State the function of the parts of the female reproductive system limited to:
– ovaries
– release of female gametes (eggs)
– oviducts
– transfers egg to uterus and the site of fertilisation
– uterus – where the fetus develops
– cervix
– ring of muscle at the opening of the uterus
– vagina
– receives penis during sexual intercourse
5 Describe fertilisation as the fusion of the nuclei from a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg cell/ovum)
9 Describe the menstrual cycle in terms of changes in the ovaries and in the lining of the uterus (knowledge of sex hormones is not required)
10 State that in early development, the zygote forms an embryo which is a ball of cells that implants into the wall of the uterus
13 State that human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection may lead to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
14 Describe the methods of transmission of HIV
15 Explain how the spread of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is controlled
Supplement
6 Compare male and female gametes in terms of size, structure, motility and numbers
7 State the adaptive features of sperm, limited to flagellum and the presence of enzymes
8 State the adaptive features of egg cells, limited to energy stores and a jelly coating that changes after fertilisation
11 State the functions of the umbilical cord, placenta, amniotic sac and amniotic fluid
12 Describe the function of the placenta and umbilical cord in relation to exchange of dissolved nutrients, gases and excretory products and providing a barrier to toxins (structural details are not required)